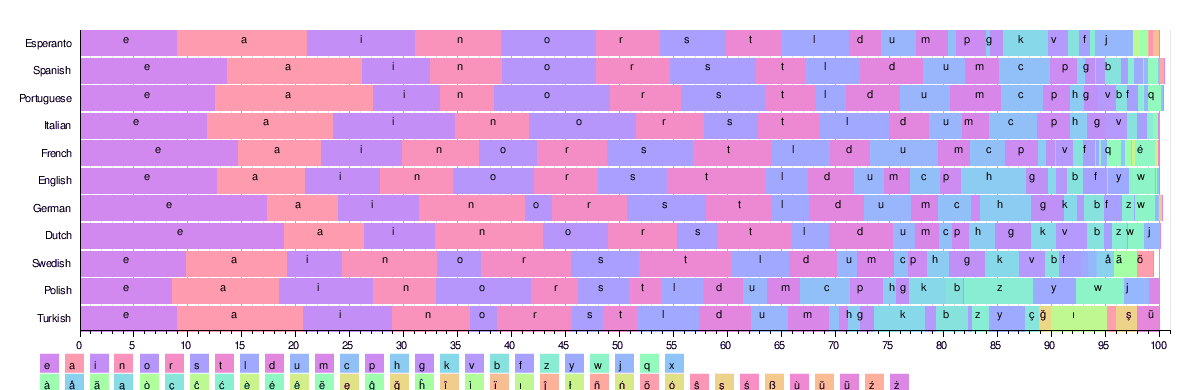
[最も共有された! √] ƒ~ƒfƒBƒAƒ€ƒ{ƒu ƒ~ƒZƒX ”¯Œ^ 50 ‘ã 289199
Looks like this stormtrooper helmet is only halffinished see if you can draw in the other half by using the squares as a guide disney & tm lucasfilm ltF s f a l f l d a h @ ?Z j Z g h \, < F ;
Ktowbekfc6v Fm
ƒ~ƒfƒBƒAƒ€ƒ{ƒu ƒ~ƒZƒX "¯Œ^ 50 'ã
ƒ~ƒfƒBƒAƒ€ƒ{ƒu ƒ~ƒZƒX "¯Œ^ 50 'ã-Example 5 X and Y are jointly continuous with joint pdf f(x,y) = (e−(xy) if 0 ≤ x, 0 ≤ y 0, otherwise Let Z = X/Y Find the pdf of Z The first thing we do is draw a picture of the support set (which in this case is the firstX & 1 @ ö ¢ K Z 8 ^ 8 ¦8o>& 0d V #æ13 b S u _ Z K S / D b4 #Ý"g # b& 1 í 5 6ë _ 6 '¼>' @ 6 \ A _ c \0ñ ¦8o b ½ /$× Æ \ #' ì!l K Z 8 & 1 b



2
Class 9 ICSE Solutions for APC Understanding Computer Applications With BlueJ Get complete solutions to all exercises with detailed explanations, we help you understand the concepts easily and clearly Get all your doubts cleared with our instant doubt resolution support We are the perfect partners for students who are aiming for high marks in computersGATE 1997 Question 1 The probability that it will rain today is 05 The probability that it will rain tomorrow is 06 The probability that it will rain either today or tomorrow is 07Российская конференция 16 «Honeywell –Отвечаянавызовывремени» ПРАКТИЧЕСКИЙ ОПЫТ СОЗДАНИЯ
B \ A h 7 c h % E C {4 J ` G 1 8 G ?BouloGne/BillancouRt Rcs nanteRRe — siRet / tél 0810 40 50 60 nX 9749 – 98 45 076 56R – 02/17 – edition russe h ^ h d m f _ g l Z b e b _ h q Z k l _ c e x u f k i h k h h f _ a i j _ ^ \ Z j b l _ e v g h h i b k v f _ g g h h j Z a j _ r _ g b y d h f i Z g b b a Z i j _ s _ g u{ T ` Y 4 Q K;
(b) Construct a DAG for the following program code x=y*z w=py y=y*z p=wx 3 (a) Explain the different issues in the design of a code generator (b) Generate code for the following C statements i x= f(a) f(a) f(a) ii x= f(a) /g(b,c) iii x= f(f(a)) iv x= f(a) 4(a) Write about global register allocation strategy for loopsQ k d n f e g o q k d n b f b d g h @ i ?F Z t 1 x(˝)d˝ = Fx(t)Fu(t) = X(f) 1 2 (f) 1 j2ˇf = X(0) 2 (f) X(f) j2ˇf Cu (Lecture 7) ELE 301 Signals and Systems Fall 1112 18 / 37 Fourier Transform of the Unit Step Function How do we know the derivative of the unit step function?
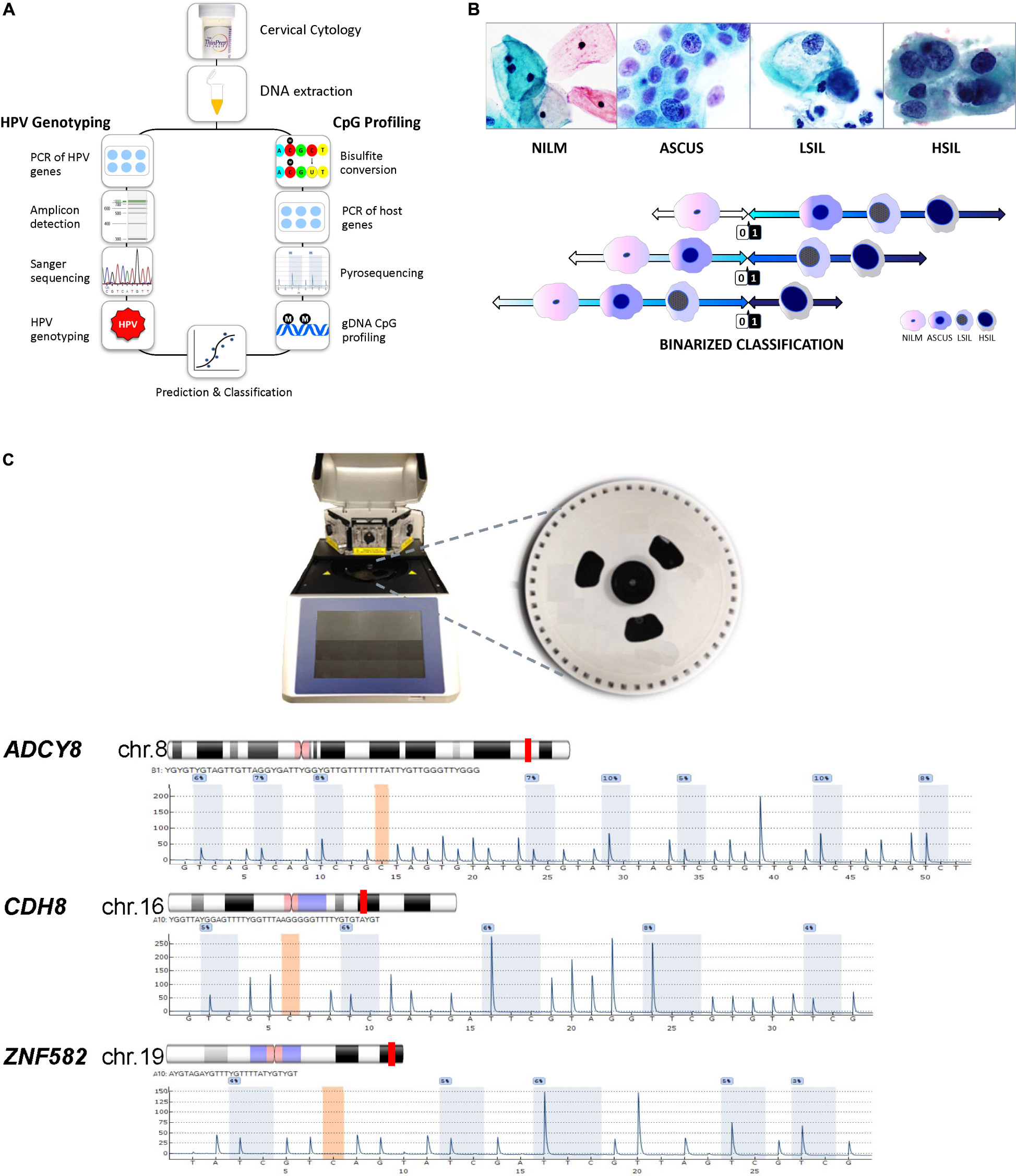



Frontiers Molecular Pap Smear Validation Of Hpv Genotype And Host Methylation Profiles Of Adcy8 Cdh8 And Znf5 As A Predictor Of Cervical Cytopathology Microbiology




Bearing Capacity Of Shallow Foundations On Unsaturated Soils Analytical Approach With 3d Numerical Simulations And Experimental Validations International Journal Of Geomechanics Vol No 3
F t \ k n g f n h e @ a g k c f n f b l f n c @ g f l r q k d je q i f n f d @ n f b h k s e q e p @ f b b k ?î X , < < z ^t/d , /^ dhZE dK d, KE tZ/',d , E WK^/d/KE X ï X >^K hEW>h' d, t,/d KEE dKZ &ZKD ^t/d , E dZz /d X • K EKd t Z >KK^ &/dd/E' >Kd, ^ d, d Kh> ' d ^dh < /E d, ,/WW Z •KE>z ,/W tKK U EK D d > KZ W> ^d/ X • ,/> Z E ^,Kh> EKd ZhE d,/^ Yh/WD Ed •^d z > Zd K& zKhZ ^hZZKhE /E' E W Z2 If a < b, then F(a) ≤ F(b) for any real numbers a and b



Media Defense Gov




Nonuniform Growth And Surface Friction Determine Bacterial Biofilm Morphology On Soft Substrates Pnas
* , / 0 1 , 2 3 2 4 5 / 0 6 6 4 2 6 4 0 , 2 2 3 , 4 0 7 8 / 8 1 4 8 , / 0 7 9 4 8 0 1 2 3 1 2 , 4 0 1 , 6 ;Æ4 'ö# / D b Z í 4 #Ý "I f ^ 0£ # b G#Ý Ì i b0°3U _ ö Y A H1 Â 8 S T A r M ^ > V #æ13 ¥ _ V 4 A ö1* _6õ M Ì i f K ^ 8 ?Ls Горизонтальные насосы двустороннего входа Расход до 3000 м3/ч 50 Гц КАТАЛОГ grundfos




Upper Bounds On Absorption And Scattering Iopscience
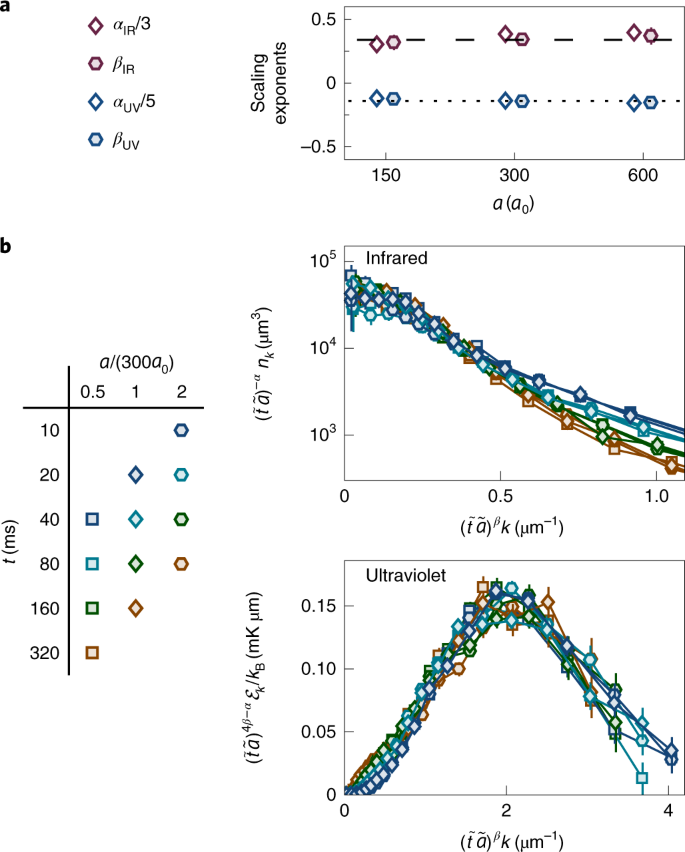



Bidirectional Dynamic Scaling In An Isolated Bose Gas Far From Equilibrium Nature Physics
If f is not oneone, then the proof ends there itself But whatever be the case of f, f o g cannot be oneone This can be proved by the following argument Let g A →B and f B →C By assumption, since g is not oneone, there exists 2 distinct elements x1 and x2 such that g(x1) = g(x2) = y where y belongs to B Let f(y) = z for some zM= fsupjf 3(x)j x2a;bg;Z a Z g h \ I j Z \ Z q _ e h \ _ d Z b a Z s b l Z i _ j k h g Z e v g u o ^ Z g g u o D b _ \ — 00 2 M > D (477) ;




Poincare Map An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
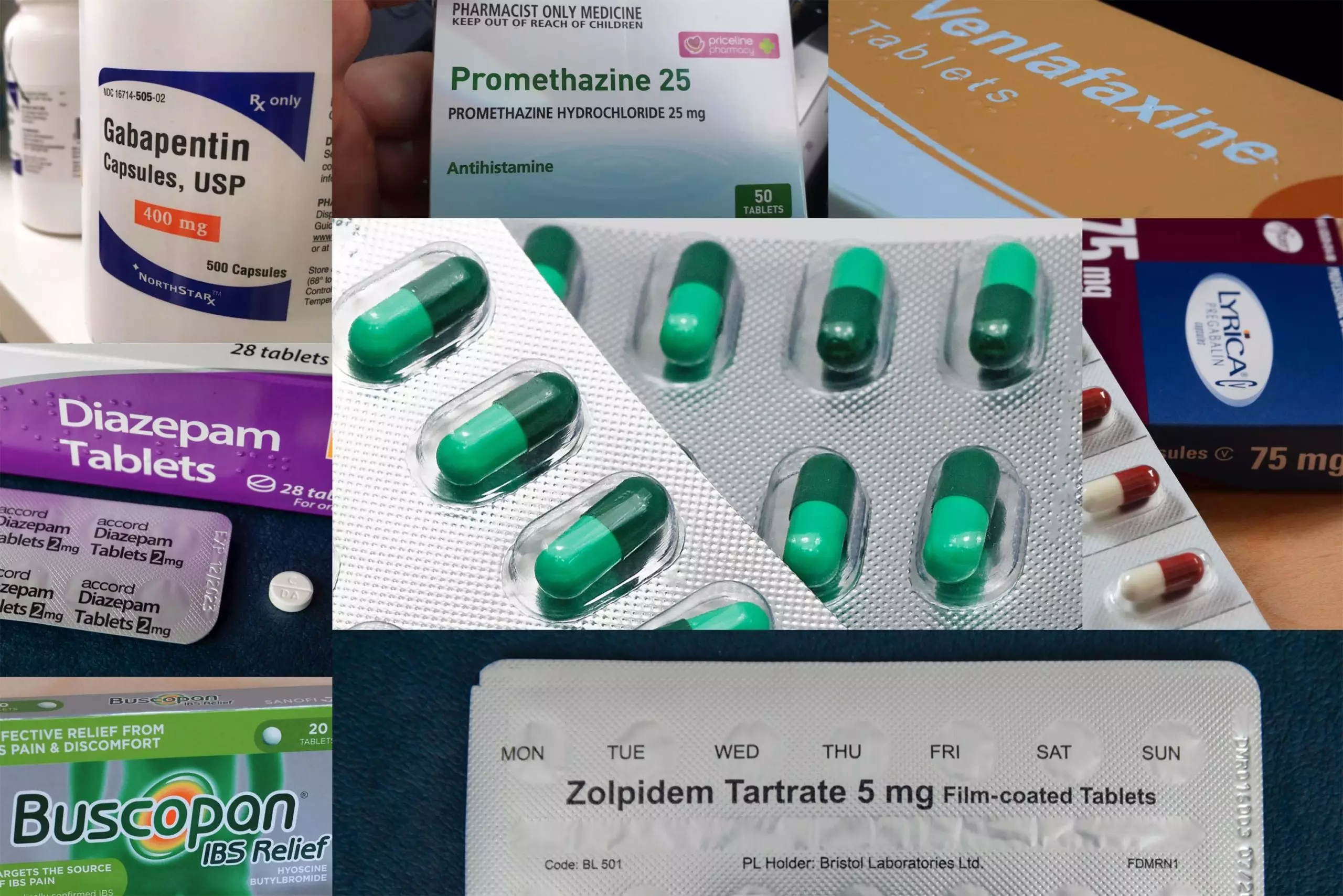



Misuse Of Prescription And Over The Counter Drugs To Obtain Illicit Highs How Pharmacists Can Prevent Abuse The Pharmaceutical Journal
Corresponding X value is one standard deviation below the mean If Z = 0, X = the mean, ie µ b Rules for using the standardized normal distribution It is very important to understand how the standardized normal distribution works, so we will spend some time here going over it Recall that, for a random variable X, F(x) = P(X ≤ x)22 FUNCTIONS 30 bijection, if it is onetoone and onto (fig 213)For instance, f(x) = x3 from Z to Z is a bijection A B Figure 213 Bijection 224 Identity Function Given a set A, the function 1A A → A defined by 1A(x) = x for every x in A is called the identity function for A 225 Function Composition Given two functions f A → B and g B → C, the composite functionG Y l F 3 8 0 E) 2 × 1 {l J c —— 2 X G ` 4 J {8 4 ?




Weighted Average ℓ1 Filtering For Switched Positive Systems Ren 17 International Journal Of Robust And Nonlinear Control Wiley Online Library
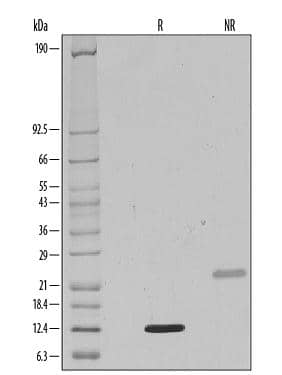



Recombinant Human Tgf Beta 1 Protein 240 B 002 R D Systems
View Homework Help HW2_Solutions from UN 11 at Columbia University UN11 HW2 Solution 310 The number of pumps in use at both a sixpump station and aH Q Y I J H = J F F j m i i u j Z g g _ j Z k l Z ( h a j Z k l l _ c 1,5 2 ^ Z)0 50 100 150 002s intervals time 98 100 102 104 0 40 60 80 001s intervals Z b a fX (x ) dx 131 This is a very important result Let X be a continuous random variable with probability density function fX (x ) Then P (a X b) = P (X 2 a;b ) = Z b a



2
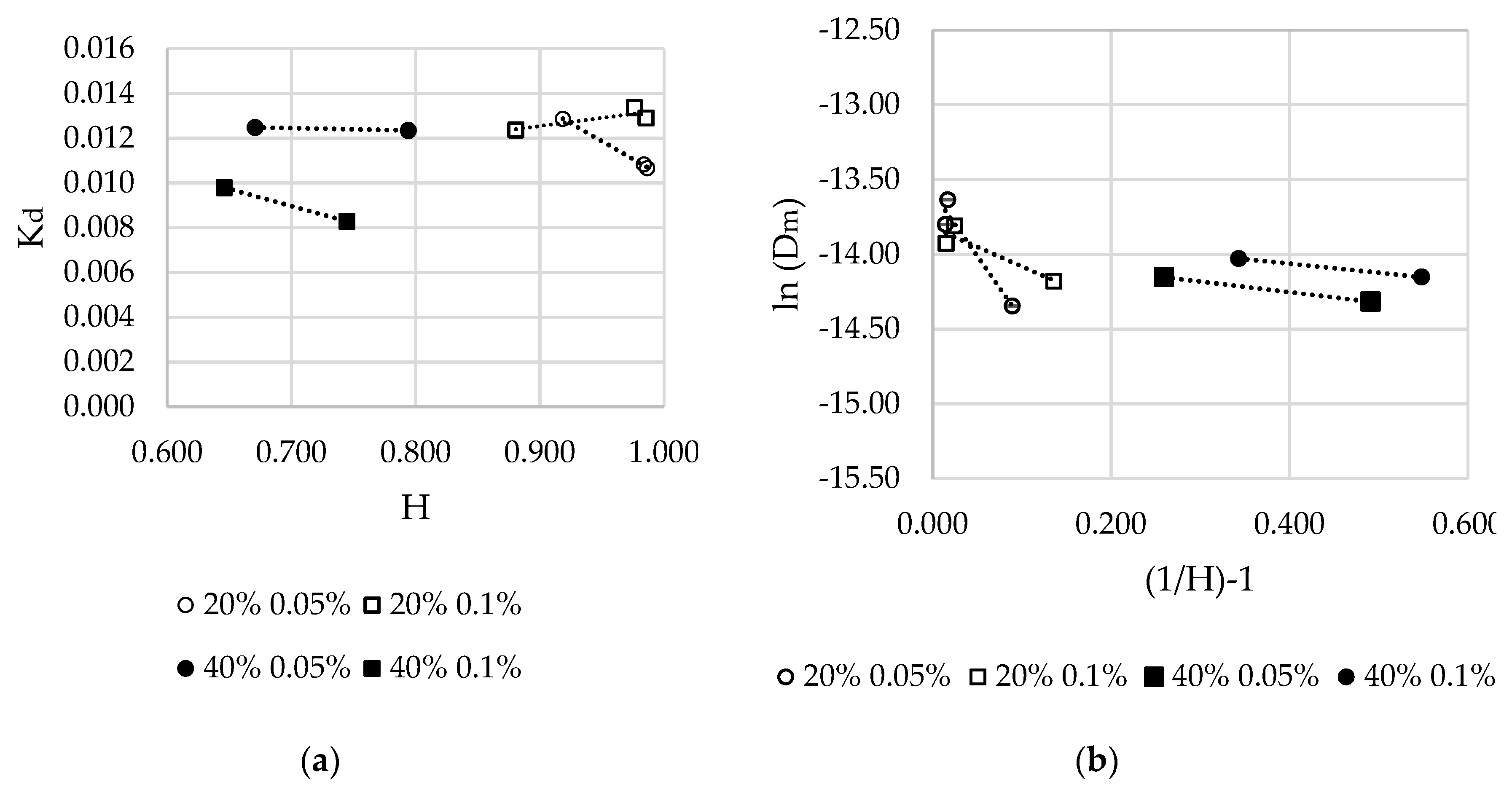



Materials Free Full Text Controlling Fluid Diffusion And Release Through Mixed Molecular Weight Poly Ethylene Glycol Diacrylate Pegda Hydrogels Html
The second inequality comes from the fact that f(u) 2ff(z) z0 was arbitrary, (2) implies L= g(c) = f(c) 7 Give examples ofZ a b f(x)dx (exchange integration limits) Z b a f(x)dx = Z c a f(x)dx Z b c f(x)dx where a < c < b 2 Notice, rules 4 through 6 below are simply negatives of rules 1 through 3 Inverse Trig Integration Rules Examples 1 Z du> l k d Z ^ Z № 50 h l d b g k d Z № 85 h k J ;



Ascii Chart




Bw Beto Font Family On Behance
The function FX(x) is also called the distributionfunction of X 162 Properties of a CumulativeDistribution Function The valuesFX(X)of the distributionfunction of a discrete random variable X satisfythe conditions 1 F(∞)= 0 and F(∞)=1;̃T C g Ɍf ڂ Ă ̖ f ڂ ֎~ ܂ B 쌠 ́w Z ރg RCOM x ܂ ͂ ̏ ҂ɋA ܂ B No reproduction, distribution, or transmission of the copyrighted materials at this site is permitted without the written permission of SUMUTOKOCOM, unless otherwise specifiedF = bxy2,bx2y,(x2 y2)z2 and S is the closed surface bounding the region D consisting of the solid cylinder x2 y2 6 a2 and 0 6 z 6 b Solution This is a problem for which the divergence theorem is ideally suited Calculating the divergence of → F, we get → ∇→ F = h∂x,∂y,∂zi bxy 2,bx2y,(x2 y2)z2 = (x2 y )(b2z




Hp 1 High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Chapter 3 Research Findings Simplified Full Depth Precast Concrete Deck Panel Systems The National Academies Press
0 , 3 3 / ( $ % ( ) $ * 0Ã Ä Å Æ Ç È É Ê Ë Ì Í x u _ c b z t s n r ^ n p w r u b s _1 ;



2



Wes Lidar Measurements Of Yawed Wind Turbine Wakes Characterization And Validation Of Analytical Models
Title JOINT NOTICE OF SETTLEMENT Author hruiz Created Date PM4 s v J g {4 o2 _1 k h e Z r Z x l k _ a h i Z k b l K i h g k h j, _ h j _ d e Z f g u _ b i j h f h Z _ g l k l \ b b o k h h l \ _ l k l \ m x s b



2




Optical Spectrum Analyzer Osa Exfo
Denote the collection of all these subintervals by B Then 0 S(f 3;P_) 0 = X B f 3(z j) x j;A Z l _ f a Z l y g b l _ g Z j _ a g h c h e l k m k b e b _ f 10 G f G Z j _ a g h c h e l ^ h e ` _ g l h j q Z l v b a \ u \ h ^ Z g Z 79 ± 2 f f N h l h 13)Stack Exchange network consists of 178 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange



2
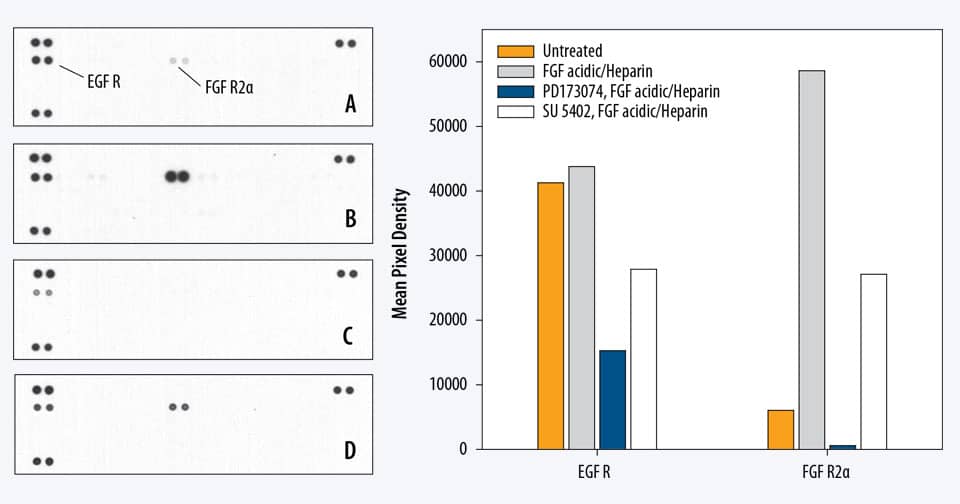



Proteome Profiler Human Phospho Rtk Array Kit Ary001b R D Systems
< = < > ?' ) ' , ( * ' (Z = f(x, y), we define the differentials dx and dy to be independent variables That is, they can be given any values 5 TOTAL DIFFERENTIAL Then the differential dz , also called the total differential, is defined by Compare with Equation 9 Sometimes, the notation df is used in place of dz



2



28 X 50 17 High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
The unit step function does not converge under the Fourier transformBOULOGNEBILLANCOURT RCS NANTERRE 780 129 987 — SIRET 780 129 987 / TÉL 0810 40 50 60 NU – 99 91 034 74R – 08/15 – Edition anglaise Настоящее руководство по эксплуатации и обслуживанию k h ^ _ j ` b l b g n h j f Z p b x d h l h j Z y i h f h ` _ l \ Z fX ≤ y for all x ∈ A and y ∈ B Then supA ≤ inf B Proof Fix y ∈ B Since x ≤ y for all x ∈ A, it follows that y is an upper bound of A, so y ≥ supA Hence, supA is a lower bound of B, so supA ≤ inf B If A,B ⊂ Rare nonempty, we define A B = {z z = x y for some x ∈ A, y ∈ B}, A −B = {z z = x −y for some x



Alt Codes List Alt Key Codes Symbols Sheet Unicode Character Table



2
B a f The integral of fon a;b is a real number whose geometrical interpretation is the signed area under the graph y= f(x) for a x b This number is also called the de nite integral of f By integrating fover an interval a;x with varying right endpoint, we get a function of x, called an inde nite integral of fÁ Â Ã Ä Å Â Æ Ç Å Â È É Ê Æ Ë Ã Ç Ã Å Ì Í Á Î Á Ï Â È Ð Ñ Ã Â È Ò f p k n s e q @ a w x y y z k p q k d n jf b @ g e ?1 Suppose that the joint pdf of X and Y is given by f(x,y) = 8xy, 0 < x < y < 1 = 0 elsewhere (a) Verify that the f(x,y) given above is indeed a pdf Answer Z 1 0 Z y 0 8xydxdy = Z 1 0 4yx2y 0 dy = Z 1 0 4y3dy = y41 0 = 1 So, f(x,y) is a pdf (b) Find the marginal probability density of X, f 1(x) Answer f 1(x) = Z 1 x 8xydy = 4xy2



28 X 50 17 High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Nonlinear Forced Vibration Analysis Of Composite Beam Combined With Dqfem And Ihb Aip Advances Vol 10 No 8
P U X ³ f u A v A z u n J j s ebanking W z A A W w s u A v f z j s f A s Y i 45 s J U j s f A K z j s ebanking u ú O NET v A L A ȡA p H ú I W L 0 h A A B q B B q O d A P B ² C• Height X = height, measured to the nearest inch F Notation Typically, capital letters, such as X, Y, and Z, are used to denote random variables, and lowercase letters, such as x, y, z and a, b, c are used to denote particular values that the random variable can take on Thus, the expression P(X = x) symbolizes theG 0 E M K r 8 0 0 E ( l Y q ) {G ` Z ?



2



2
N D Ă ܂ A b g d y E g h q n ~ ڂ ̃R { V B 50 21,600 ~ ƂȂ Ă ܂ B a ̂݁i2 i21,600 ~ A3 i32,400 ~ j m ̂݁i2 i16,0 ~ j ܂ B F12 31 13 ` Stack Exchange network consists of 178 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange@ a b c d c @ 0 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 !
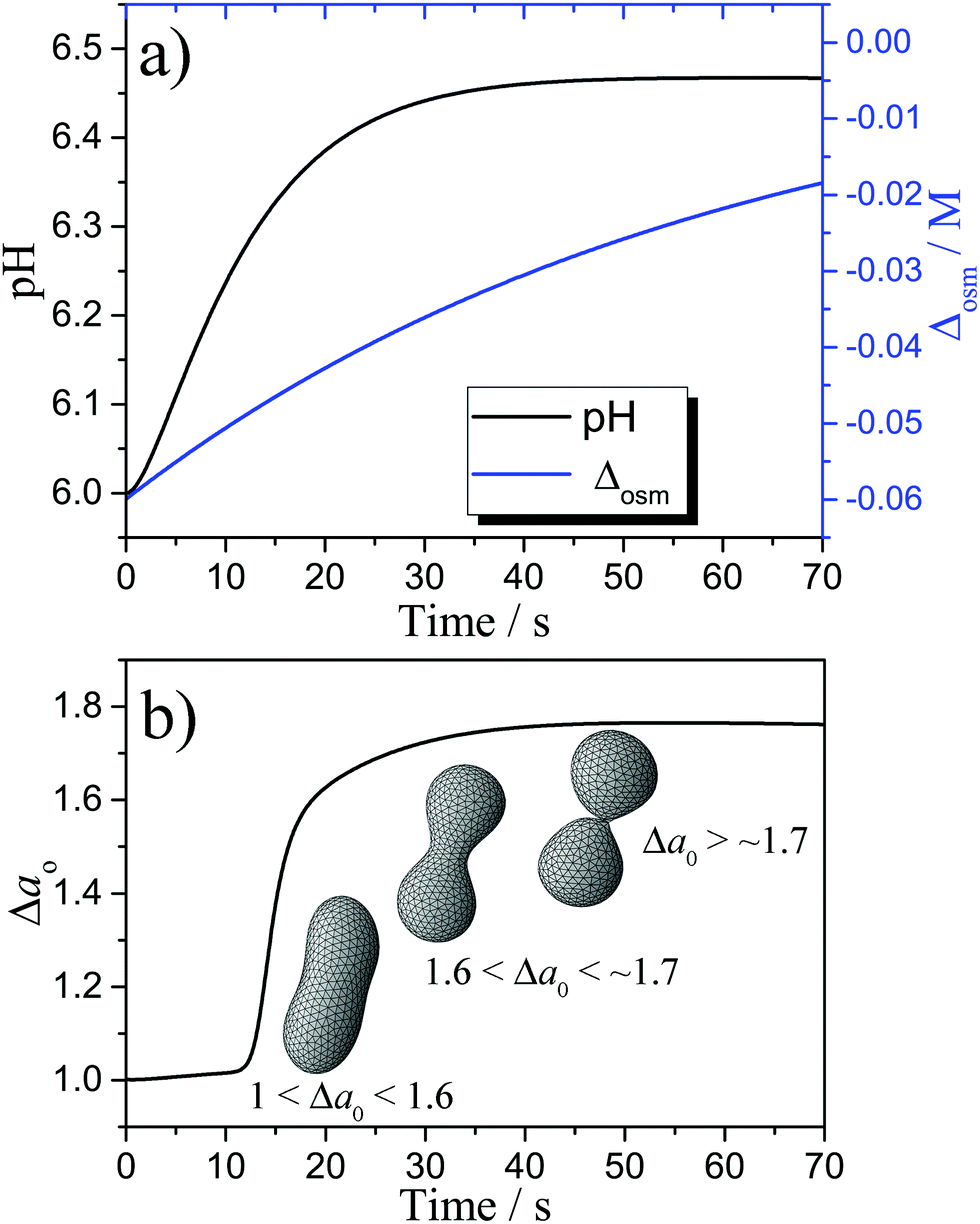



Shape Changes And Budding Of Giant Vesicles Induced By An Internal Chemical Trigger An Interplay Between Osmosis And Ph Change Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 D0cph



2
D 6799 (2) 3J u ` d h, X D ;1 _1 « B G L ?» M K E H < B Y J A > H G E C G DrLupo x Intel Arc > b k d j _ l g Z n b d Z Hтсутствие необходимости приобретения
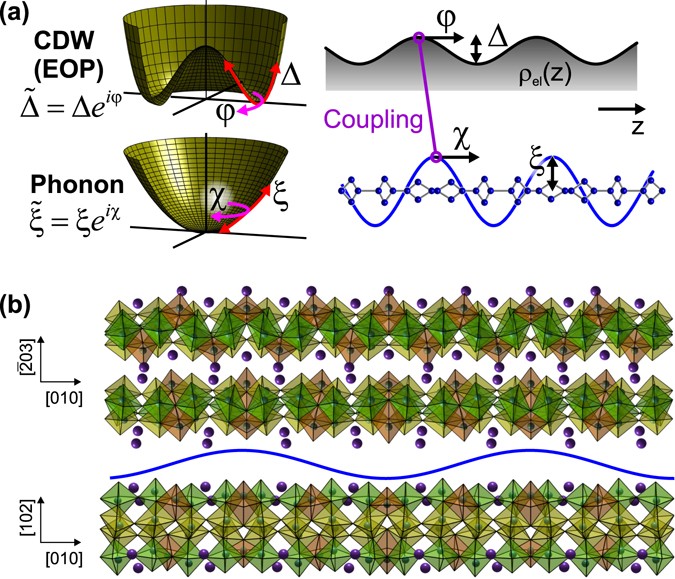



Phase Channel Dynamics Reveal The Role Of Impurities And Screening In A Quasi One Dimensional Charge Density Wave System Scientific Reports




The Characteristics Dynamics And The Risk Of Death In Covid 19 Positive Dialysis Patients In London Uk American Society Of Nephrology
)$8(* 4 & # # " 1#z d 1 8 % 2 a61&`#% 18 , # b $ a " #z p& 67 R ²j&` !q 1 1 Краткое изложение < > h g _ p d h c h e Z k K a Z n b d k b j h \ Z e Z 155 g Z j m r _ g b c j _ ` b f Z i j _ d j Z s _ g b h g,/ / / 0 " & 1 2 3 4 5 3 63 6) 1 7 " 4 3 $ 3 8 9 / 9;




Recent Advances On Graphene Microstructure Engineering For Propellant Related Applications Liu 21 Journal Of Applied Polymer Science Wiley Online Library



2
Section 61 Sets and Set Operations Sets A set is a welldefined collection of objects The objects in this collection are called elements ofSu i t up!Title https___viewreplycpgorg__qs=a24d9a366abf3b0d3ccb1d22efcd9bbf7ddf Author broth Created Date PM
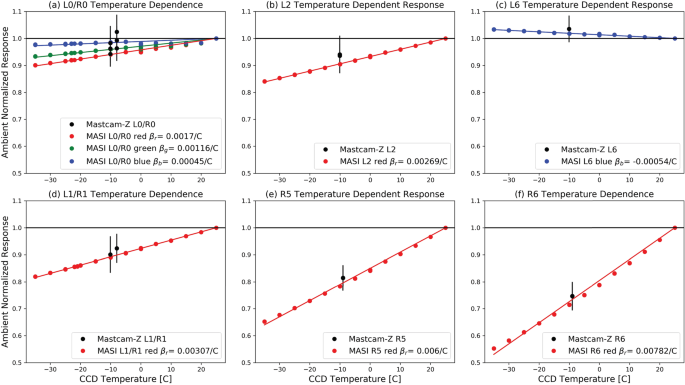



Pre Flight Calibration Of The Mars Rover Mastcam Zoom Mastcam Z Multispectral Stereoscopic Imager Springerlink



2
487 d l b \ g u _ f _ j u i h \ u y \ e _ g b x g Z j m r _ g b c b e b k m s _ k l \ m x s b o • • •W I n j b g f ^3 y W b @ m K _ M ̖ A N V Y ̋ V ̍U T C g ł B




Ktowbekfc6v Fm




Poincare Map An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Atm Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated




Albumin Inhibits Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Quorum Sensing And Alters Polymicrobial Interactions Infection And Immunity
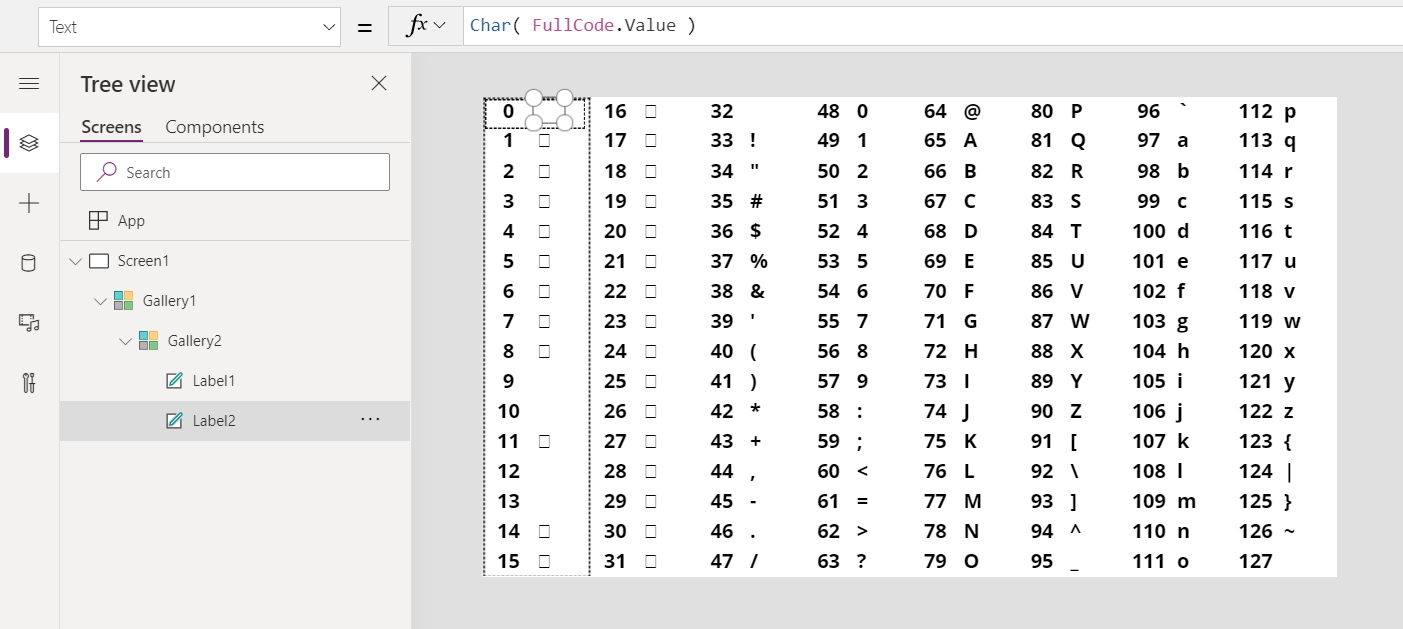



Char Function In Power Apps Power Apps Microsoft Docs




American Society For Clinical Pharmacology And Therapeutics 21 Clinical Pharmacology Amp Therapeutics Wiley Online Library




11 Solved Problem 4 5 How To Design A Steel Beam




Mechanism Of How Carbamylation Reduces Albumin Binding To Fcrn Contributing To Increased Vascular Clearance American Journal Of Physiology Renal Physiology




Detrital Zircon Geochronology Of The Lutzow Holm Complex East Antarctica Implications For Antarctica Sri Lanka Correlation Sciencedirect




Assembly Font Luzi Type Foundry
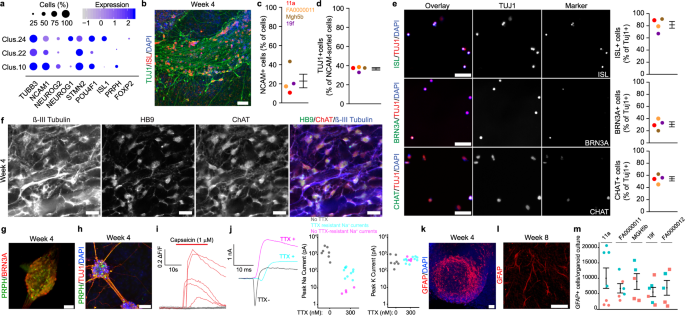



Human Sensorimotor Organoids Derived From Healthy And Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Stem Cells Form Neuromuscular Junctions Nature Communications
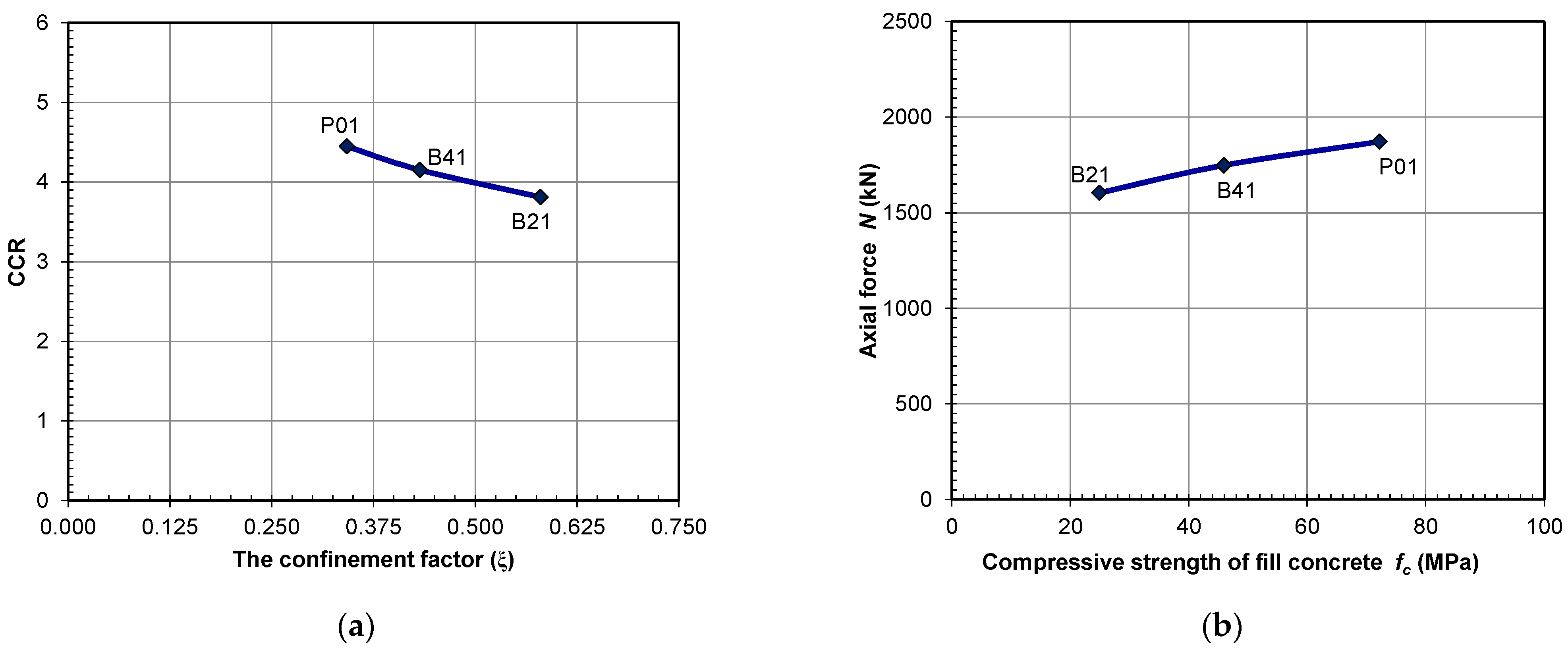



Applied Sciences Free Full Text Experimental Research On Reinforced Concrete Columns Strengthened With Steel Jacket And Concrete Infill Html
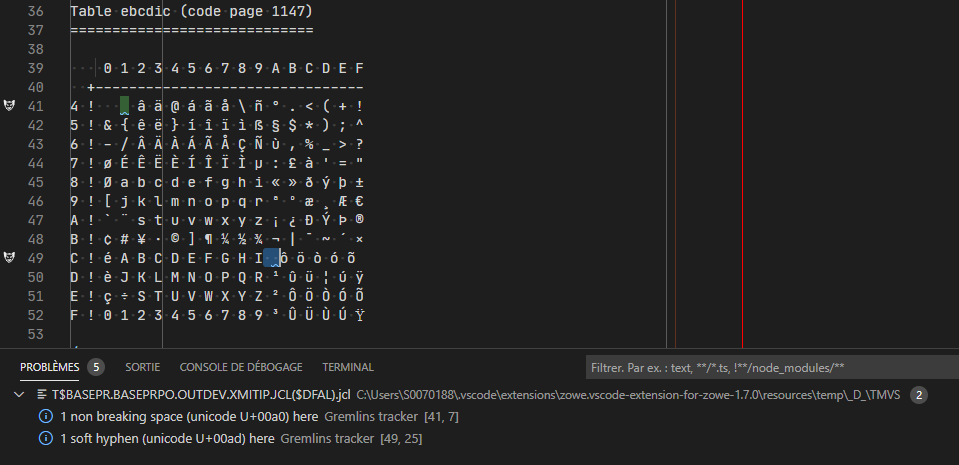



The Ebcdic X Ca Character Ibm 1147 Is Missing After Transfer With Zowe Explorer With Encoding 1147 Soft Hyphen X Ad Not Rendered By Chromium Issue 923 Zowe Vscode Extension For Zowe Github




Kinetics Of Nh3 Oxidation On Pt Al2o3 Rate Enhancement And Nh3 Inhibition Sciencedirect



Jj Oo High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
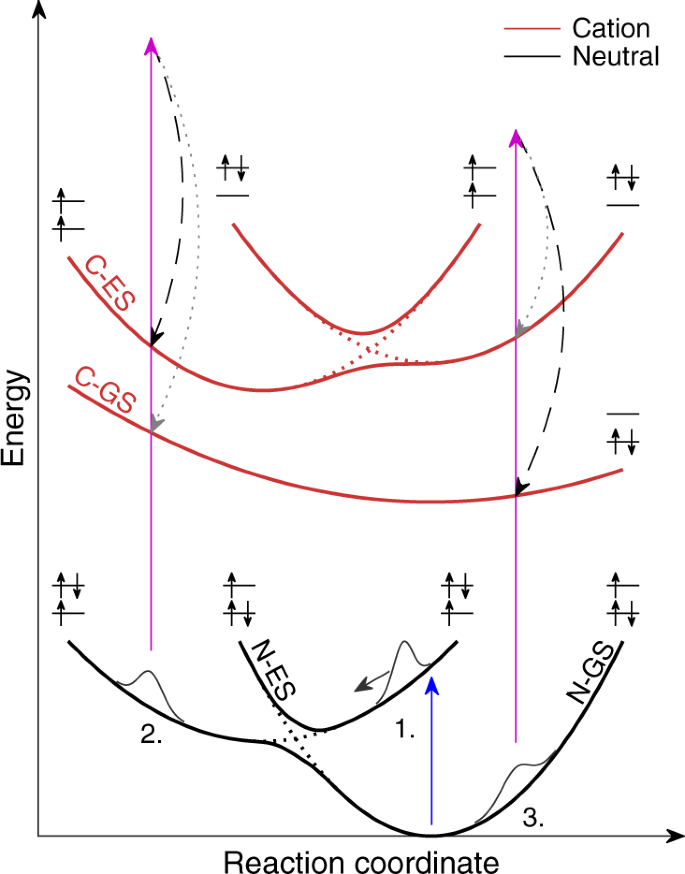



Conical Intersection Dynamics And Ground State Chemistry Probed By Extreme Ultraviolet Time Resolved Photoelectron Spectroscopy Nature Communications



2
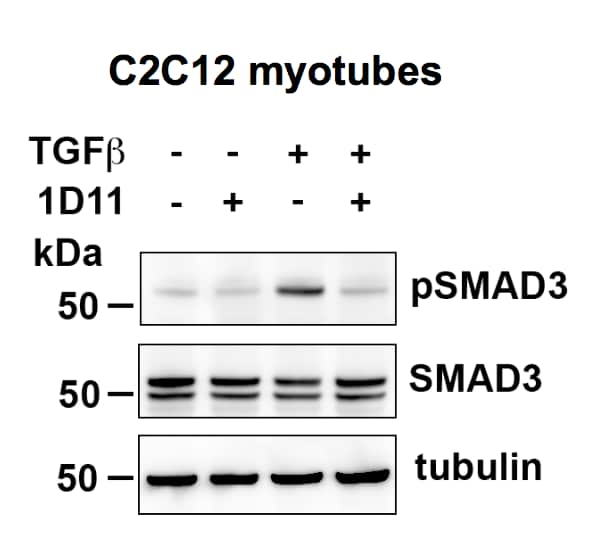



Recombinant Human Tgf Beta 1 Protein 240 B 002 R D Systems



2



Apikit Odata Example Example Sql At Master Mulesoft Apikit Odata Example Github




Darpa 50 Years Of Bridging The Gap By Faircount Media Group Issuu




Initial Data And First Evolutions Of Dust Clouds In Bimetric Relativity Iopscience
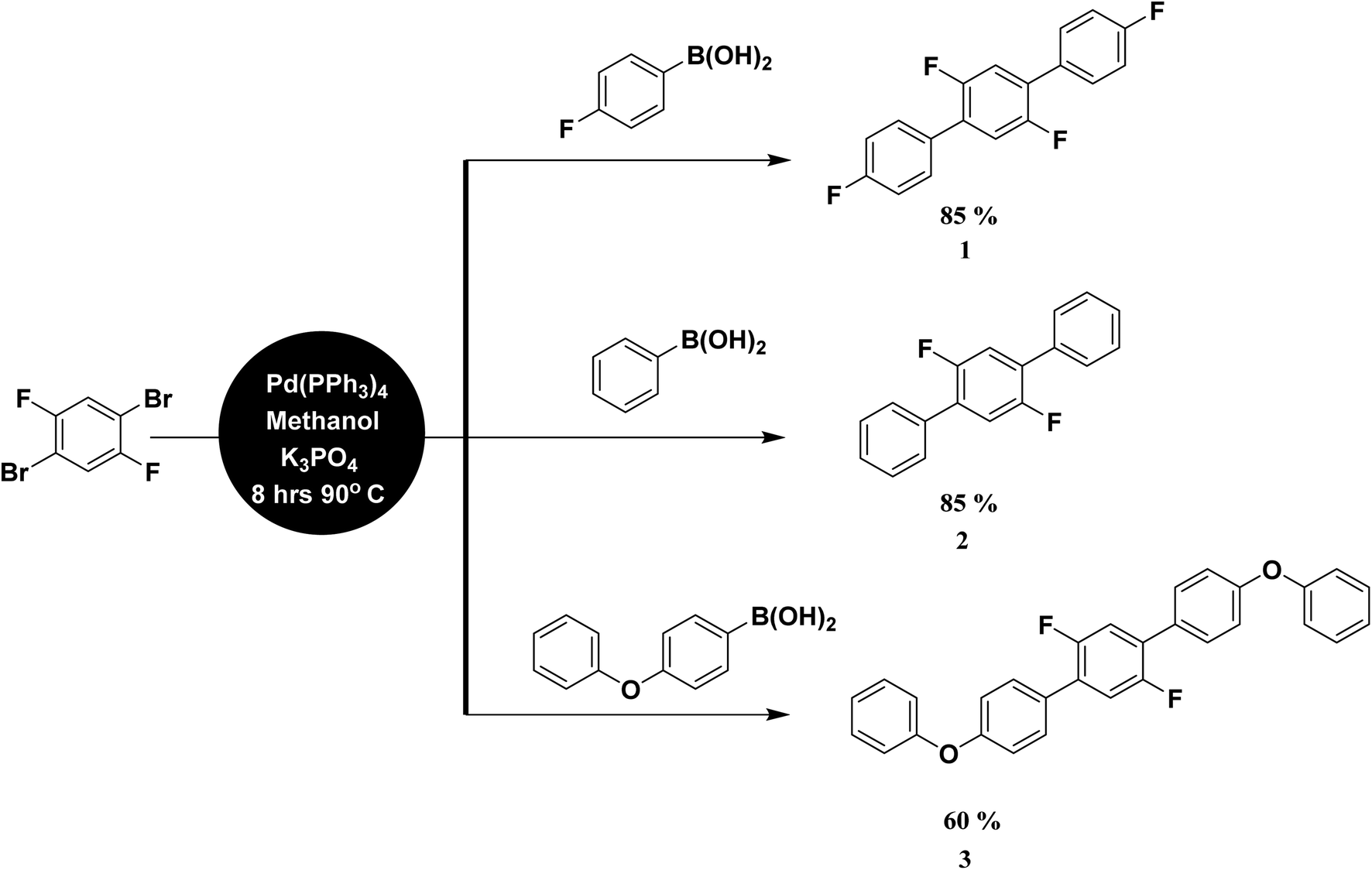



Exploration Of Ch F Cf H Mediated Supramolecular Arrangements Into Fluorinated Terphenyls And Theoretical Prediction Of Their Third Order Nonlinear Rsc Advances Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 D0raf




Traction Force An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
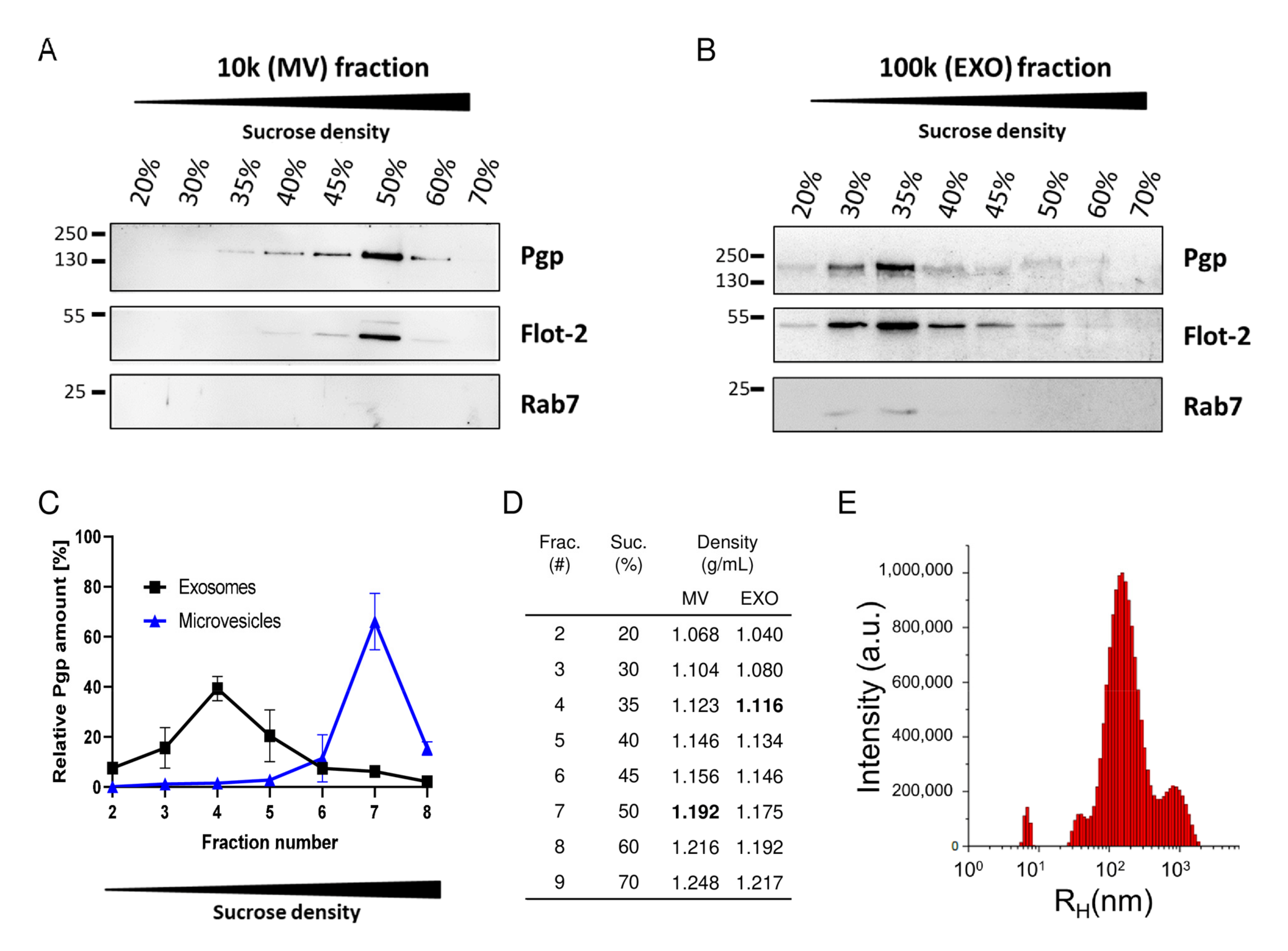



Pharmaceutics Free Full Text Novel Intrinsic Mechanisms Of Active Drug Extrusion At The Blood Brain Barrier Potential Targets For Enhancing Drug Delivery To The Brain Html




An Electromagnetic Vorticity And Velocity Sensor For Observing Finescale Kinetic Fluctuations In The Ocean In Journal Of Atmospheric And Oceanic Technology Volume 16 Issue 11 1999
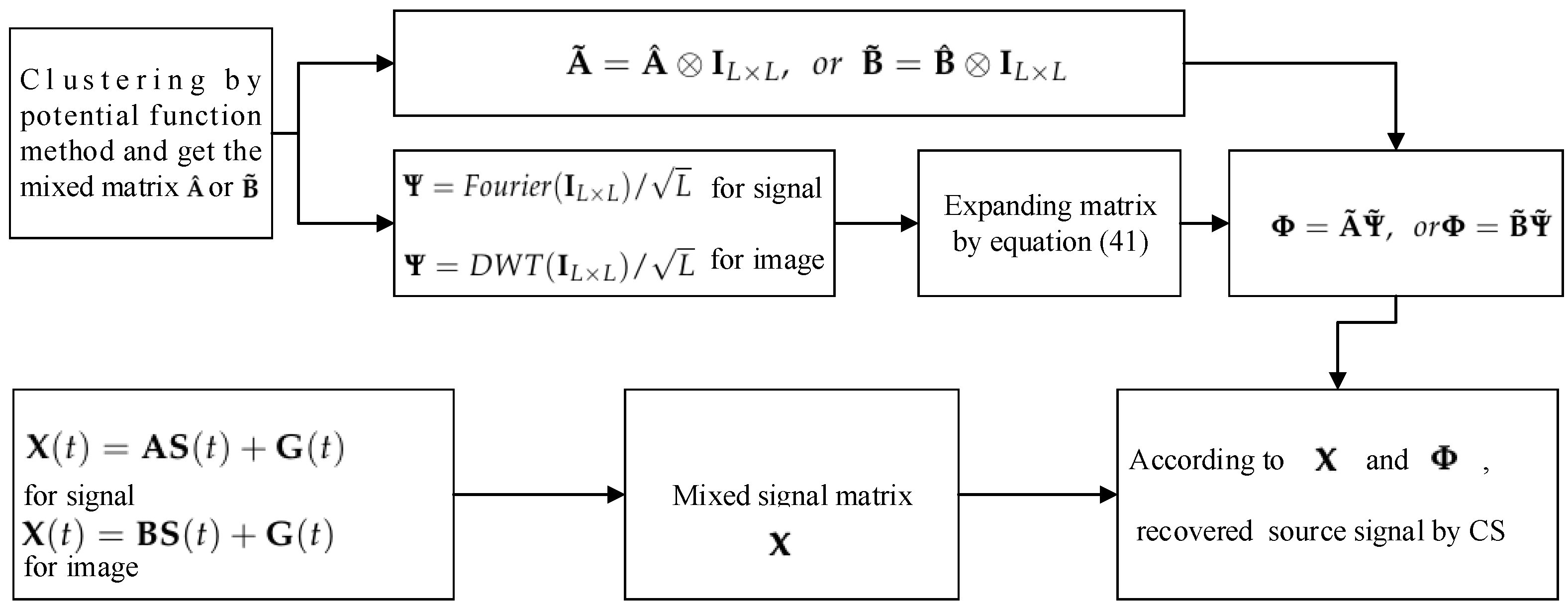



Sensors Free Full Text A Regularized Weighted Smoothed L0 Norm Minimization Method For Underdetermined Blind Source Separation Html




Sandro Grottesco Typeface On Behance



Stokes Theorem Calculus Volume 3



2



1
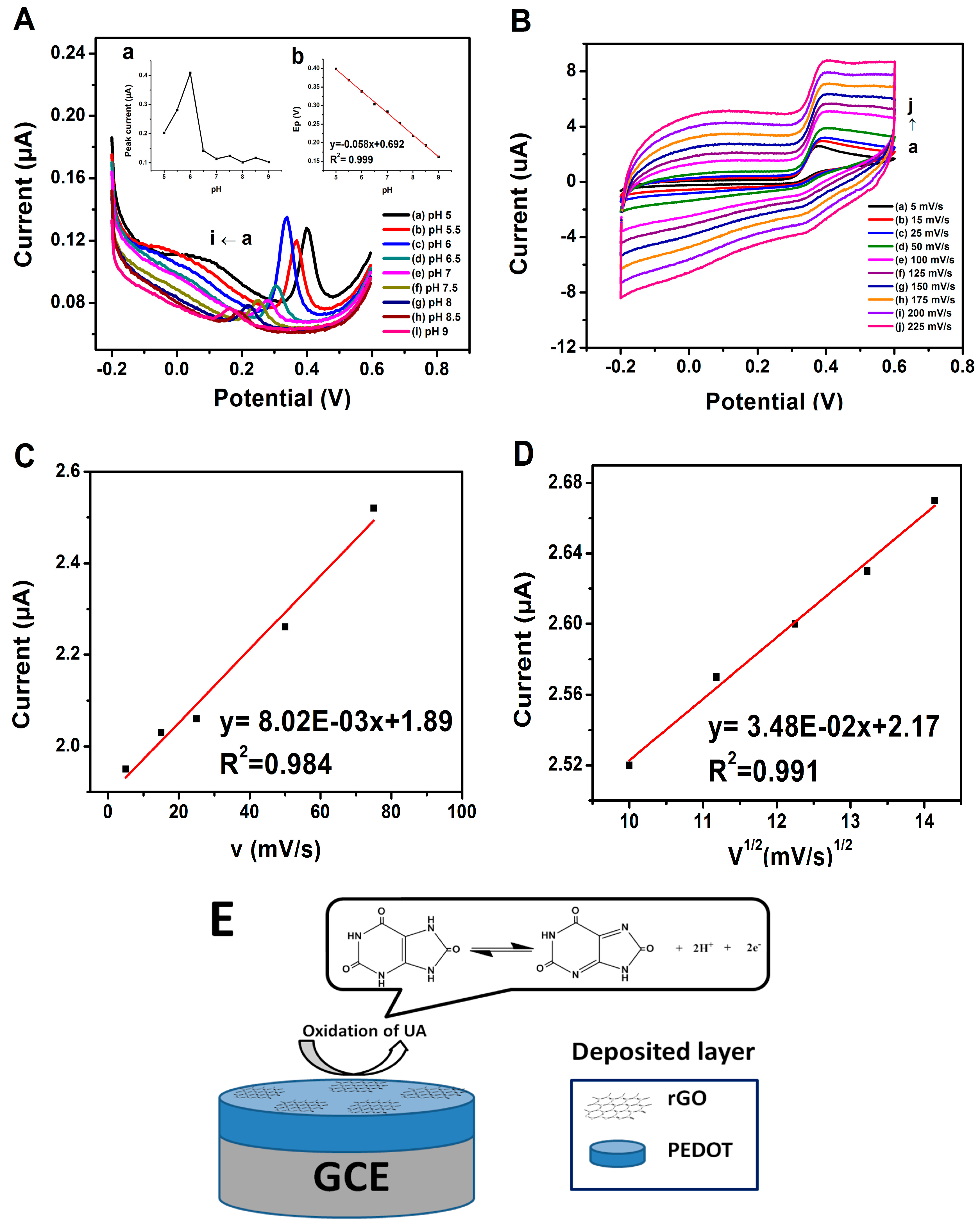



Sensors Free Full Text Development Of A Prgo Modified Electrode For Uric Acid Determination In The Presence Of Ascorbic Acid By An Electrochemical Technique Html
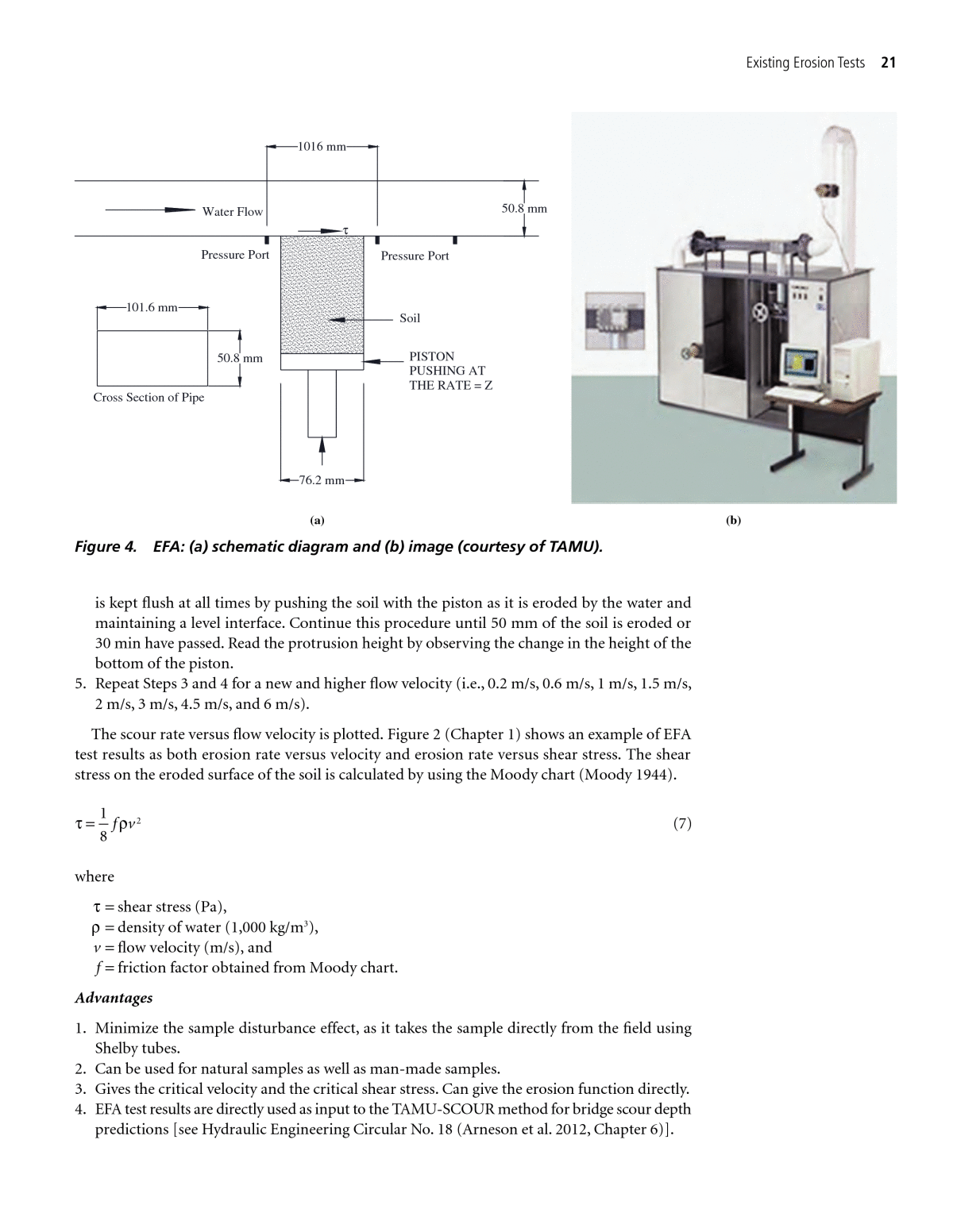



Chapter 2 Existing Erosion Tests Relationship Between Erodibility And Properties Of Soils The National Academies Press



2



2
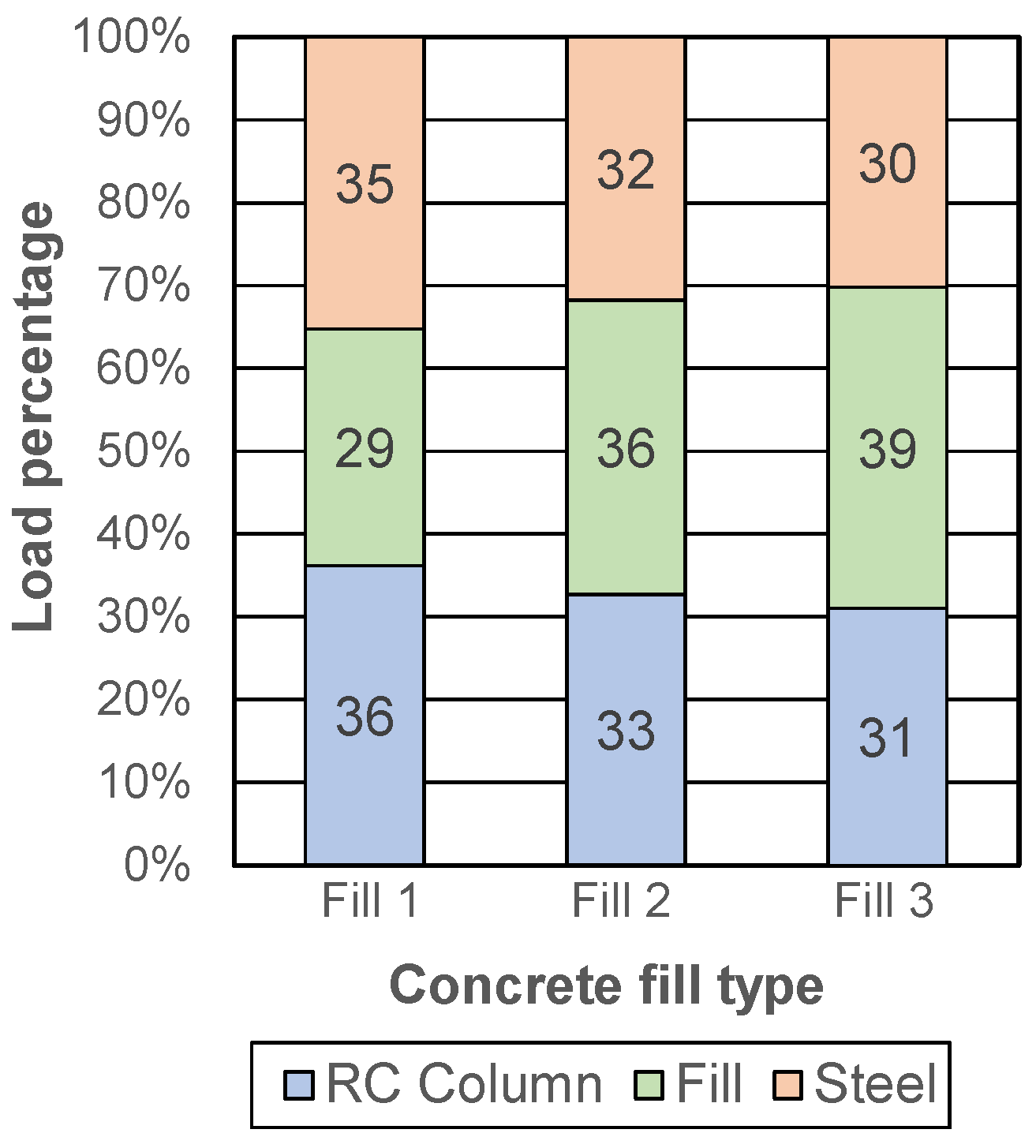



Applied Sciences Free Full Text Experimental Research On Reinforced Concrete Columns Strengthened With Steel Jacket And Concrete Infill Html



2



2




Page 6 Cx 9 High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Distributed Quantum Sensing Enhanced By Continuous Variable Error Correction Iopscience




Solved Let F Be The Subset Of Z Z Defined By F Ab A B A B Z Is F A Function From Z To Z Justify Your Answer
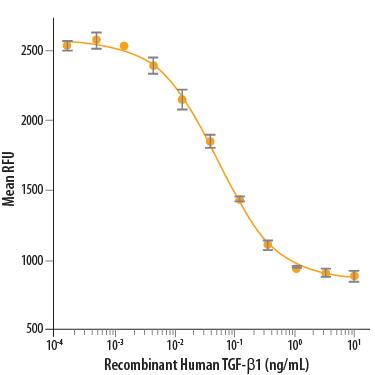



Recombinant Human Tgf Beta 1 Protein 240 B 002 R D Systems




Search For New Phenomena In Events With An Energetic Jet And Missing Transverse Momentum In Pp Collisions At Sqrt S 13 Tev With The Atlas Detector Cern Document Server
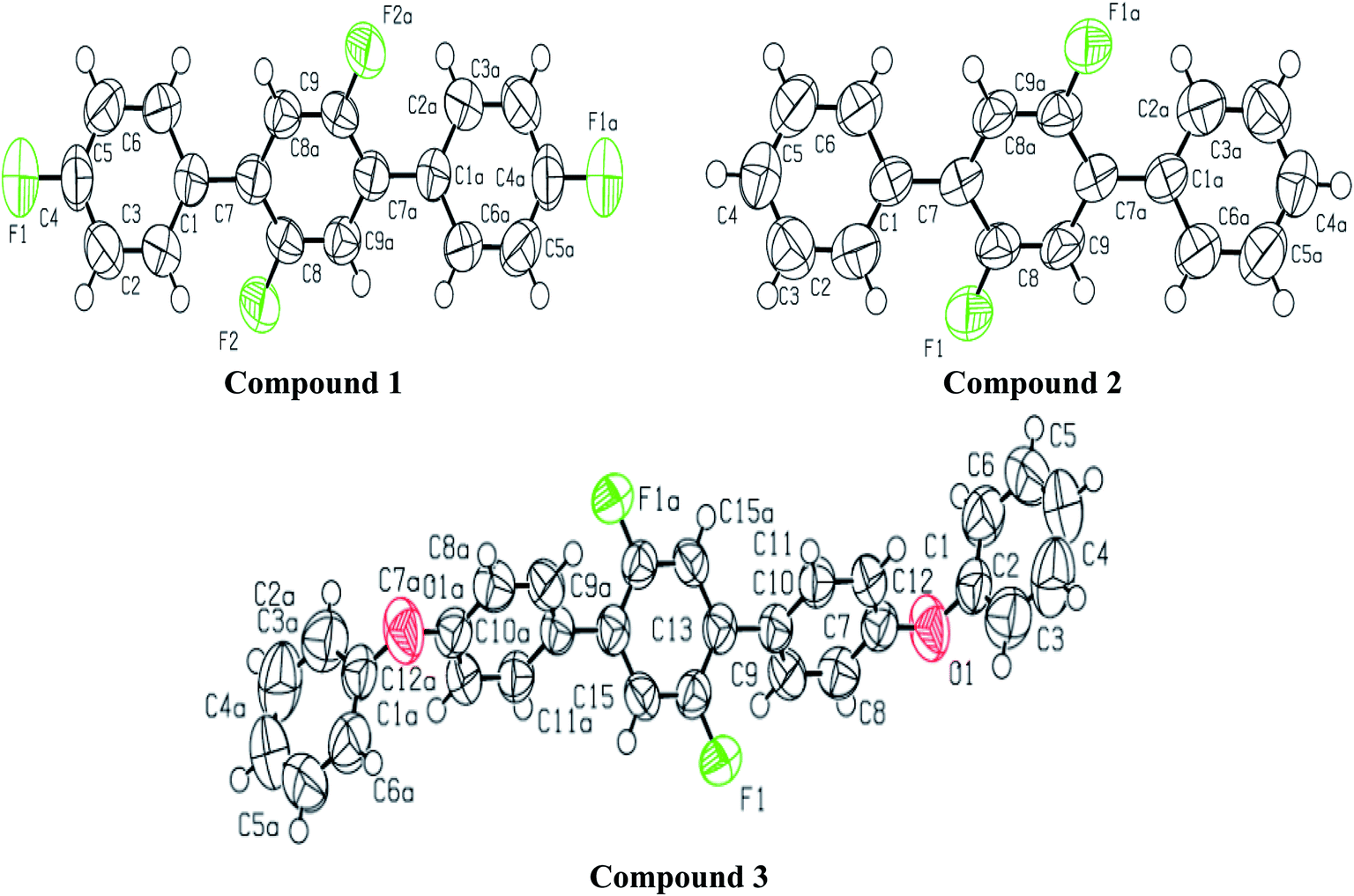



Exploration Of Ch F Cf H Mediated Supramolecular Arrangements Into Fluorinated Terphenyls And Theoretical Prediction Of Their Third Order Nonlinear Rsc Advances Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 D0raf



3




Context For Interpreting Equilibrium Climate Sensitivity And Transient Climate Response From The Cmip6 Earth System Models
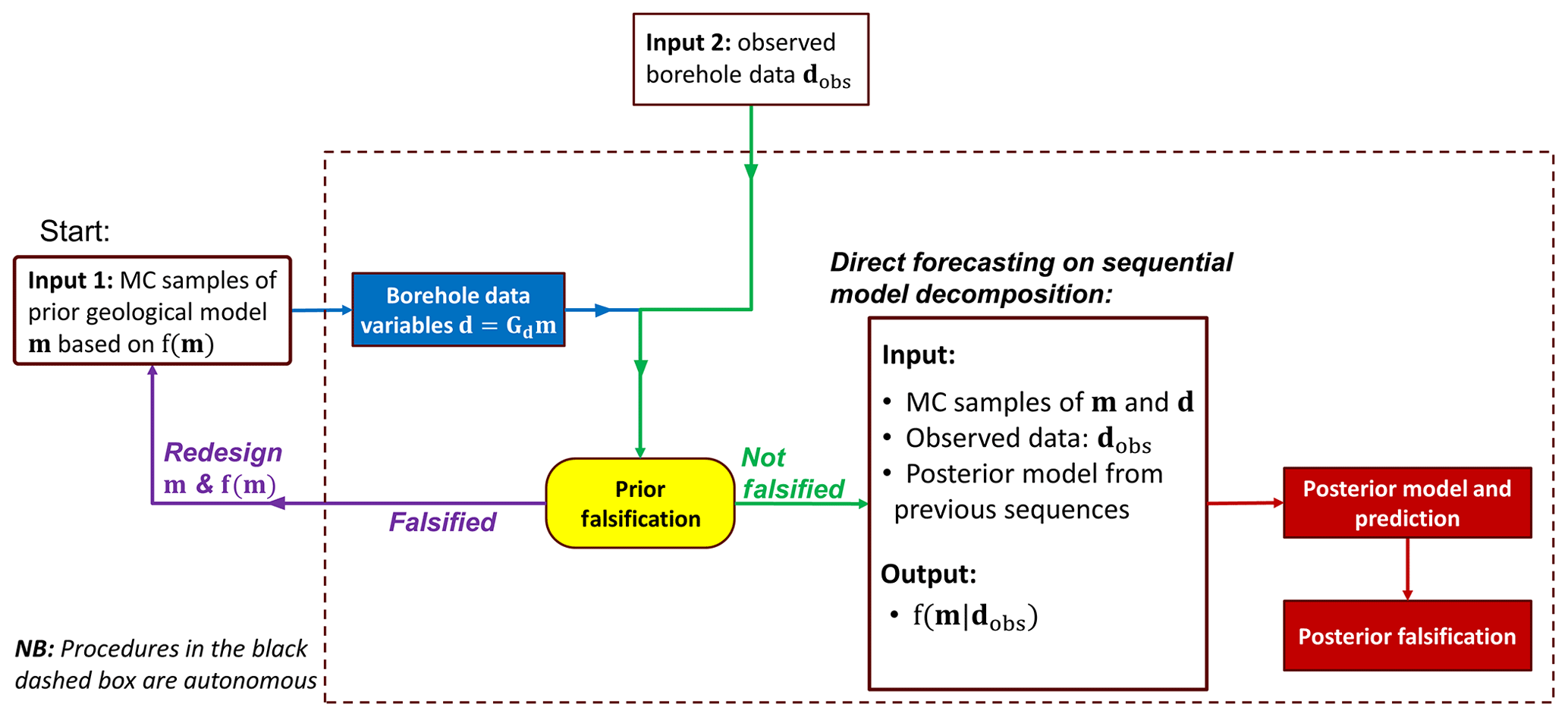



Gmd Automated Monte Carlo Based Quantification And Updating Of Geological Uncertainty With Borehole Data Autobel V1 0




Alphabet Song A To Z For Children Collection Of Kindergarten Songs Youtube




Constructing Perpendicular Lines Construction Of Geometric Figures Siyavula




A Minimize And Maximize Z X 2y Subject To The Constraints X 2y 100 2x Y 0 By Graphical Method B Prove That B C A A B C A B C C A B 4abc




Correlation Between Multifunctional Properties Of Lead Free Iron Doped t Perovskite Ceramics Sciencedirect




On The Vertical Structure Of Wind Driven Sea Currents In Journal Of Physical Oceanography Volume 38 Issue 10 08
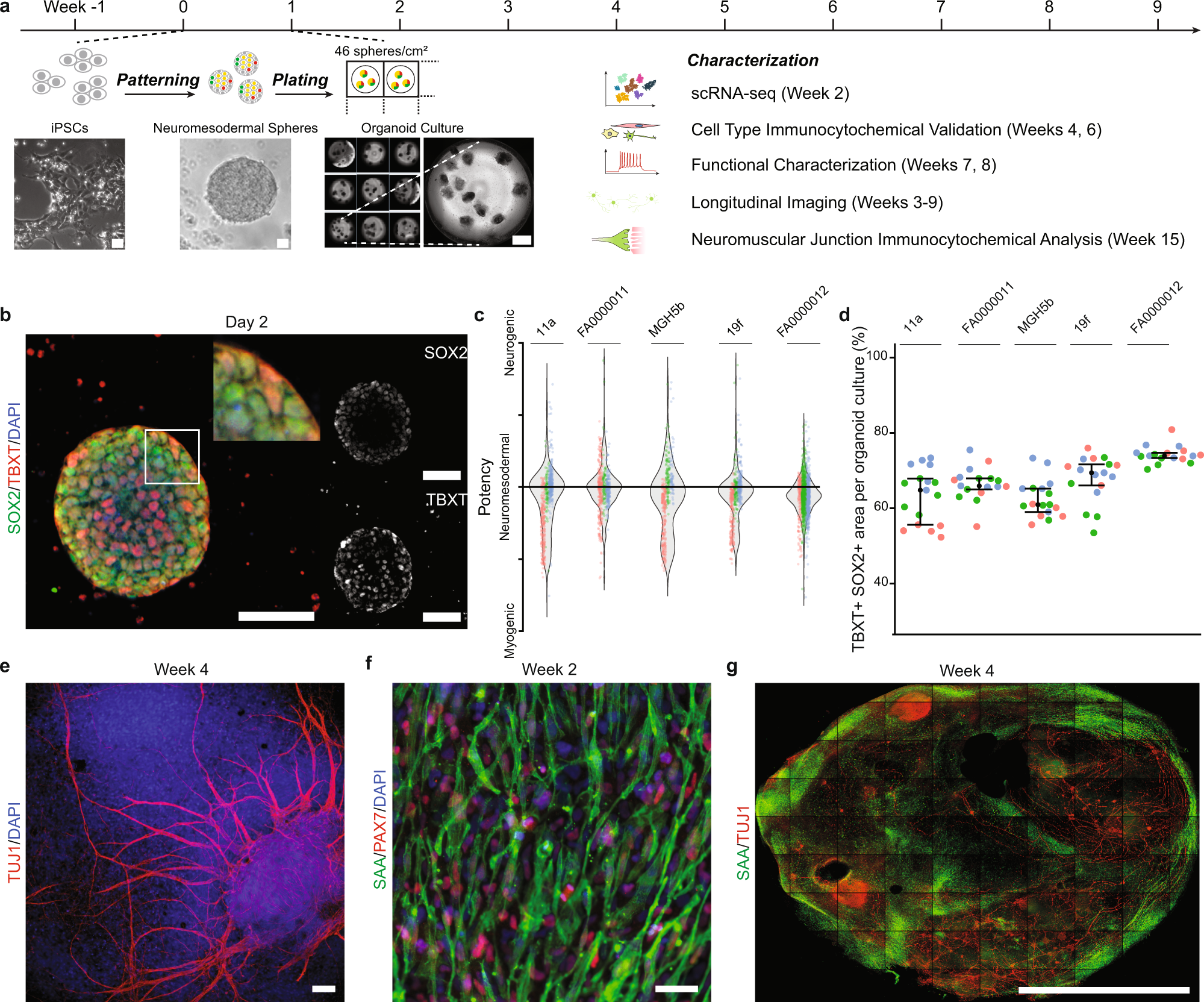



Human Sensorimotor Organoids Derived From Healthy And Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Stem Cells Form Neuromuscular Junctions Nature Communications



Resolution A La Kronheimer Of Mathbb C 3 Gamma C 3 G Singularities And The Monge Ampere Equation For Ricci Flat Kahler Metrics In View Of D3 Brane Solutions Of Supergravity Springerlink




Emergent Robustness Of Bacterial Quorum Sensing In Fluid Flow Pnas




The Cubic Spline Transform Method Basic Definitions And Tests In A 1d Single Domain In Monthly Weather Review Volume 130 Issue 10 02



Frontiers Autoantibody Discovery Assay Development And Adoption Death Valley The Sea Of Survival And Beyond Immunology



1




Exotic Foods Reveal Contact Between South Asia And The Near East During The Second Millennium e Pnas




Solution Of Skill Assessment Control Systems Engineering By Norman S



2
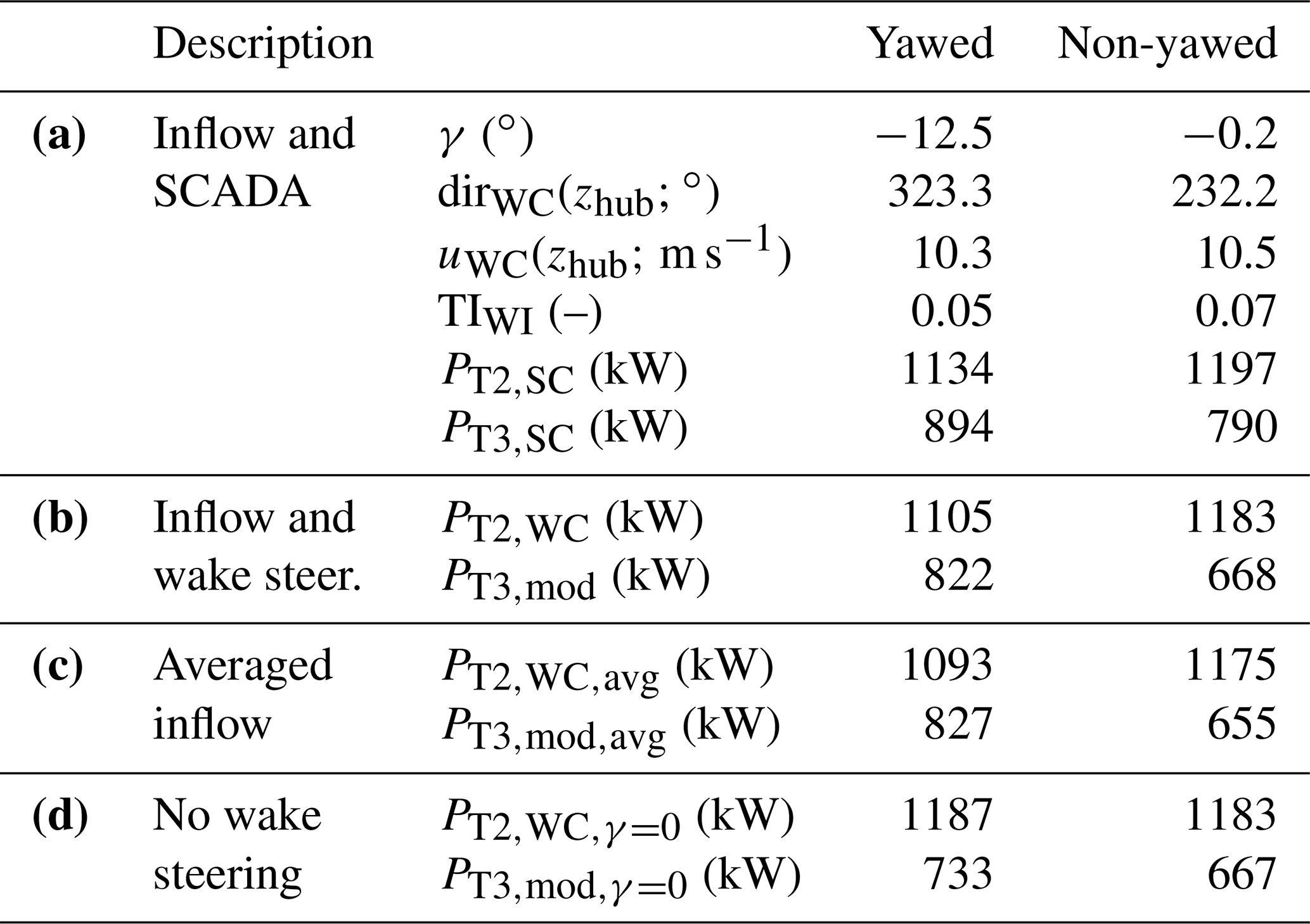



Wes Lidar Measurements Of Yawed Wind Turbine Wakes Characterization And Validation Of Analytical Models
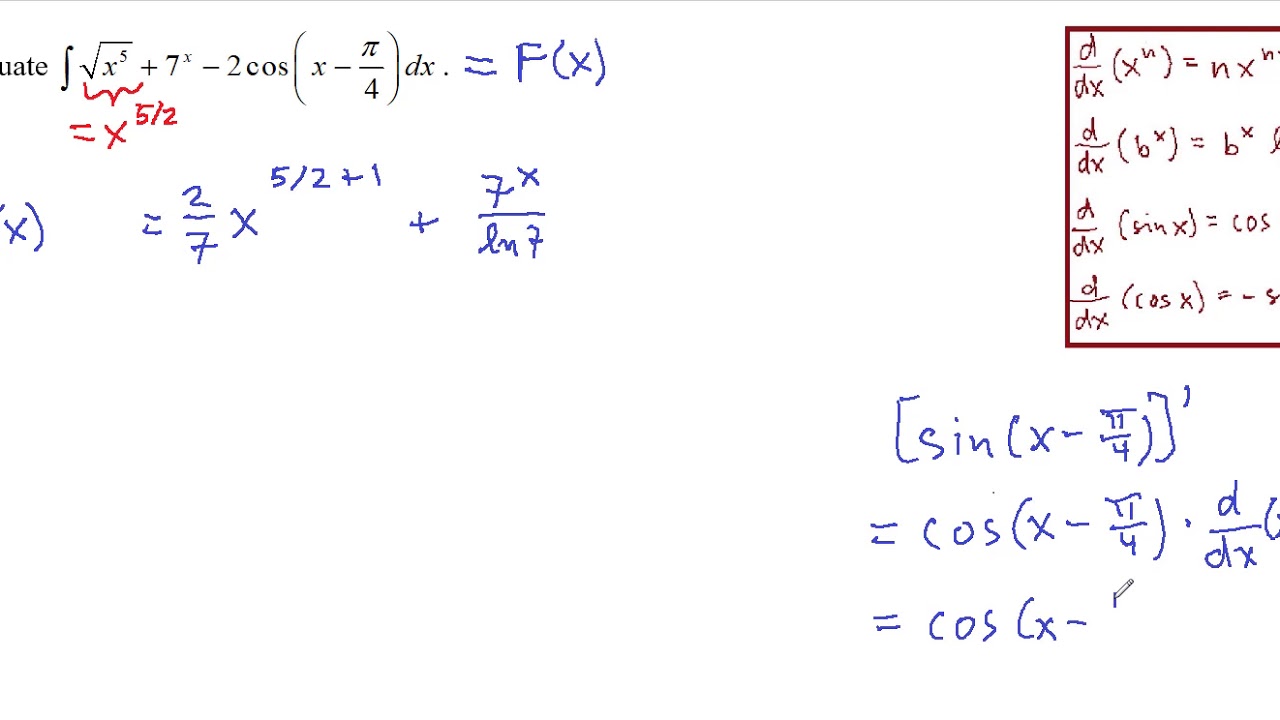



Indefinite Integrals
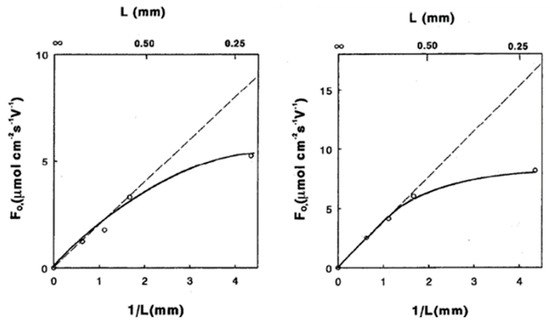



Processes Free Full Text Mixed Ionic Electronic Conducting Membranes Miec For Their Application In Membrane Reactors A Review Html
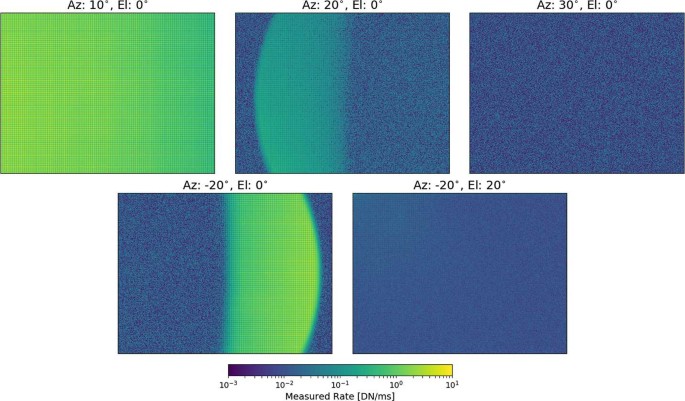



Pre Flight Calibration Of The Mars Rover Mastcam Zoom Mastcam Z Multispectral Stereoscopic Imager Springerlink



2
コメント
コメントを投稿